 MPEG
Activities MPEG
Activities
MPEG-21 Part
7: Digital Item Adaptation
Introduction
to MPEG-21 [1]
Today,
many elements exist to build an infrastructure for the delivery and
consumption of multimedia content. There is, however, no 'big picture'
to describe how these elements, either in existence or under development,
relate to each other. The aim for MPEG-21 is to describe how these various
elements fit together. Where gaps exist, MPEG-21 will recommend which
new standards are required. ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 (MPEG) will then
develop new standards as appropriate while other relevant standards
may be developed by other bodies. These specifications will be integrated
into the multimedia framework through collaboration between MPEG and
these bodies.
The
vision for MPEG-21 is to define a multimedia framework to enable
transparent and augmented use of multimedia resources across a wide
range of networks and devices used by different communities.
Digital Item
Adaptation Overview [1]
The
goal of the Terminals and Networks key element is to achieve interoperable
transparent access to (distributed) advanced multimedia content by shielding
users from network and terminal installation, management and implementation
issues. This will enable the provision of network and terminal resources
on demand to form user communities where multimedia content can be created
and shared, always with the agreed/contracted quality, reliability and
flexibility, allowing the multimedia applications to connect diverse
sets of Users, such that the quality of the user experience will be
guaranteed.
The
Digital Item Adaptation tools in this specification are clustered into
seven major categories as illustrated in Figure 1. The categories are
clustered according to their functionality and use for Digital Item
Adaptation around the Schema Tools and Low-Level Data Types. The schema
tools provide uniform root elements for all DIA descriptions as well
as some low-level and basic data types which can be used by several
DIA tools independently.:
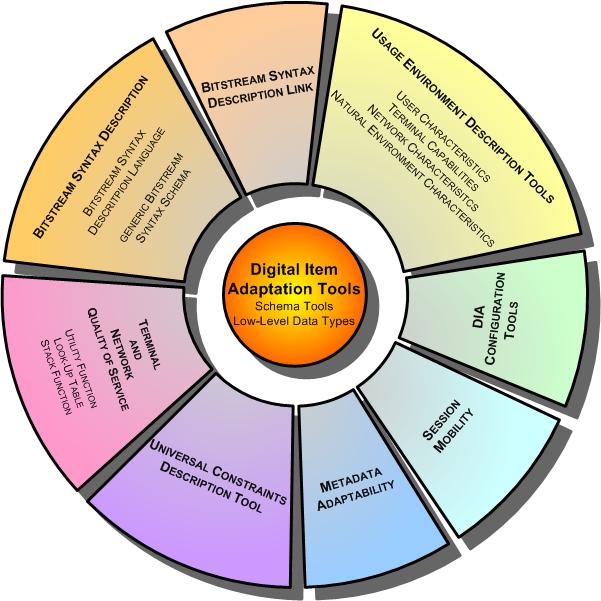
Figure
1 — Digital Item Adaptation Overview
The
first major category is the Usage Environment Description Tools,
which include User characteristics, terminal capabilities, network characteristics
and natural environment characteristics. These tools provide descriptive
information about these various dimensions of the usage environment,
which originate from Users, to accommodate, for example, the adaptation
of Digital Items for transmission, storage and consumption.
The
second category is referred to as BSDLink which provides
the facilities to create a rich variety of adaptation architectures
based on tools specified within this part of ISO/IEC 21000, ISO/IEC
21000-2, and ISO/IEC 15398 among others.
Bitstream Syntax Description Tools comprise the third
major category of Digital Item Adaptation tools. A BSD describes the
syntax – in most cases, the high level structure – of a
binary media resource. Using such a description, a Digital Item resource
adaptation engine can transform the bitstream and the corresponding
description using editing-style operations such as data truncation and
simple modifications.
The fourth category of tools is referred to as Terminal and
Network Quality of Service. The description tools specified
in this category describe the relationship between QoS constraints (e.g.,
on network bandwidth or a terminal’s computational capabilities),
feasible adaptation operations satisfying these constraints and associated
media resource qualities that result from adaptation. This set of tools
therefore provides the means to trade-off these parameters with respect
to quality so that an adaptation strategy can be formulated and optimal
adaptation decisions can be made in constrained environments.
The Universal Constraints Description Tool form the
fifth category of tools which enables the possibility to describe limitation
and optimisation constraints on adaptations.
The sixth category is referred to as Metadata Adaptability.
This description tool specifies hint information that can be used to
reduce the complexity of adapting the metadata contained in a Digital
Item. On the one hand they are used for filtering and scaling and on
the other hand for integrating XML instances.
For Session Mobility, the seventh category of tools,
the configuration state information that pertains to the consumption
of a Digital Item on one device is transferred to a second device. This
enables the Digital Item to be consumed on the second device in an adapted
way.
Finally, the eighth category of tools are referred to as DIA
Configuration Tools which provides information required for
the configuration of an Digital Item Adaptation Engine.

Our
Contribution
A
proposal of generic bitstream syntax description together with Siemens
Munich. This approach enables resource format independent bistream synatx
descriptions to be constructed [4][5].
In December 2003 we reached Final Draft International Standard [3]
stage (including our contribution:-).
For
more information please send an email to christian.timmerer@itec.uni-klu.ac.at.
Links:
References
and Public Documents
[1]
Jan Bormans, Keith Hill , MPEG-21
Overview v.4, doc. N5231, Shanghai, China, October 2002
[2] Editor: Anthony Vetro, Requirements
for Digital Item Adaptation, doc. N4684, Jeju, Korea, March 2002
[3] Editors: Anthony Vetro, Christian Timmerer,
and Sylvain Devillers, ISO/IEC 21000-7 FDIS: MPEG-21 Digital Item Adaptation,
doc. N6168, Waikoloa, Hawaii, December 2003
[4] C. Timmerer, G. Panis, H. Kosch, J. Heuer, H.
Hellwagner, A. Hutter: Coding format independent multimedia content
adaptation using XML, In: Proceedings of SPIE International Symposium
ITCom 2003 on Internet Multimedia Management Systems IV, Vol. 5242 Orange
County Convention Center, Orlando, Florida, USA, 7-11 September 2003
[5] Gabriel Panis, Andreas Hutter, Jörg Heuer,
Hermann Hellwagner, Harald Kosch, Christian Timmerer, Sylvain Devillers
and Myriam Amielh, Bitstream Syntax Description: A Tool for Multimedia
Resource Adaptation within MPEG-21, In: EURASIP Signal Processing: Image
Communication, Special Issue on Multimedia Adaptation
|

